API Access#
1. API Token Generation#
To use the MailTrigger HTTP API, you must first generate an API Token. Follow these steps:
Log in to MailTrigger and click the user avatar at the top right → User Settings.
From the sidebar, click API Tokens.
Click Generate New Token: - Name (optional): Provide a label to identify this token. - Click Create.
The system will display the newly created token only once. Be sure to copy and store it securely.
If lost, go back to the API Tokens list, click Revoke for the lost token and generate a new one.
2. Authentication (No Username/Password Support)#
All MailTrigger API requests require authentication via API Token. Username and password are not supported.
HTTP Headers Include the following headers in every API request:
Authorization: Bearer <YOUR_API_TOKEN> Content-Type: application/json
Example
curl -X GET https://app.mailtrigger.app/v1/domains \ -H "Authorization: Bearer abcdef1234567890" \ -H "Content-Type: application/json"
Error Responses - Missing or invalid tokens will result in HTTP
401 Unauthorized. - Expired or revoked tokens may return401or403 Forbidden.
Note
API Tokens grant full access to your account. Never expose them in public code or frontend environments.
For automated or scheduled access, store tokens securely in environment variables or a secrets manager.
MailTrigger API Reference#
Available APIs#
Note
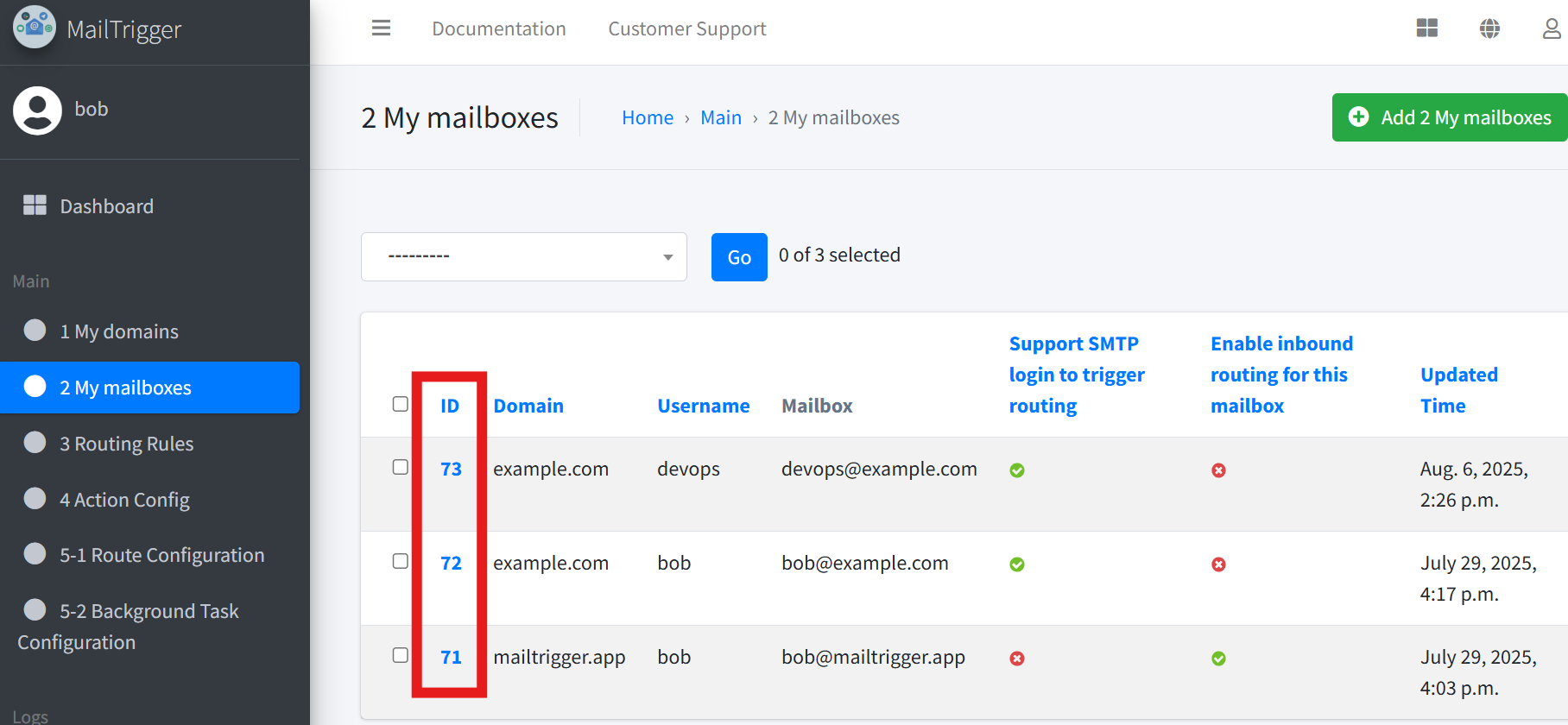
For all endpoints that require an {id} (such as mailbox id, domain id, or rule id),
you can find the corresponding ID directly in the MailTrigger web interface.
For example, to find a mailbox id, go to Mailboxes, then you will see the mailboxes list. The mailbox IDs will be shown on that page.
Note
MailTrigger provides a full API documentation. Please log in to your account and visit:
https://app.mailtrigger.app/swagger/
There you can browse all available APIs and see detailed specifications, including request/response formats and parameter definitions.
DOMAINS#
/api/v1/domains/
Manage user domains.
Methods: GET, POST
/api/v1/domains/{id}/
Retrieve or modify a specific domain.
Methods: GET, PUT, PATCH, DELETE
MAILBOXES#
/api/v1/mailbox/
Manage user mailboxes.
Methods: GET, POST
/api/v1/mailbox/{id}/
Retrieve or modify a specific mailbox.
Methods: GET, PUT, PATCH, DELETE
GET /api/v1/mailbox/{mailboxId}/archives/
Retrieve all archived emails (sent and received) of a specific mailbox.
Methods: GET
Filter Parameters:
sender: Filter by sender (case-insensitive, partial match supported)receivers: Filter by receiver(s) (case-insensitive, partial match supported)subject: Filter by subject (case-insensitive, partial match supported)body: Filter by email body (case-insensitive, partial match supported)hasAttachments: Filter by presence of attachments (True/False)date_after/date_before: Filter by email sending date rangedate_exact: Filter by exact sending datecreatedTime_after/createdTime_before: Filter by archive creation datesearch: Global search across sender, receivers, subject, body, attachments, and content
Usage Examples:
Filter emails with subject containing “Meeting” and with attachments:
GET /api/v1/mailbox/123/archives/?subject=Meeting&hasAttachments=True
Filter emails sent between August 1–20, 2024:
GET /api/v1/mailbox/123/archives/?date_after=2024-08-01&date_before=2024-08-20
Global search for “project” keyword:
GET /api/v1/mailbox/123/archives/?search=project
/api/v1/mailbox/{mailboxId}/data/
Retrieve or manage custom receiver data configured for a mailbox.
Methods: GET, POST, PUT, PATCH, DELETE
Filter Parameters (for GET):
file: Filter by file IDemails: Filter by email(s), comma-separatednote: Filter by note content (case-insensitive, partial match supported)data: Search JSON key-value pairs (case-insensitive, partial match supported)fields: Return only selected JSON fields (comma-separated)created_after/created_before: Filter by data creation date rangecreated_exact: Filter by exact creation datesearch: Global search in email, note, and all JSON fields
Usage Examples (GET):
Filter data with note containing “urgent”:
GET /api/v1/mailbox/123/data/?note=urgent
Filter data created on August 15, 2024:
GET /api/v1/mailbox/123/data/?created_exact=2024-08-15
Search for
status: activein JSON data:GET /api/v1/mailbox/123/data/?data=status:active
Return only
emailandnamefields:GET /api/v1/mailbox/123/data/?fields=email,name
/api/v1/mailbox/{id}/logs/
Read or append mailbox processing logs.
Methods: GET, POST
/api/v1/mailbox/{id}/testmail/
Send a test message to the mailbox.
Methods: POST
/api/v1/mailbox/{id}/actions/{actionConfigId}/wasmfile/
Download the WASM file for a specific mailbox–action configuration.
Methods: GET
/api/v1/mailbox/{id}/tasks/{taskId}/wasmfile/
Download the WASM file associated with a specific mailbox task.
Methods: GET
/api/v1/mailbox/{id}/mail/send/
This endpoint allows you to send an email using the specified mailbox. The request must be authenticated with a valid API token belonging to the owner of that mailbox.
Methods: POST
Request Body Parameters:
to(string | list)Recipient email address or a list of recipient addresses.
subject(string)Subject line of the email.
body(string)Content of the email body.
password(string)The password of the mailbox, required to authorize sending.
Example Request:
{ "to": ["user1@example.com", "user2@example.com"], "subject": "Test Email", "body": "This is a test email sent via API.", "password": "example-password" }
RULES#
/api/v1/rules/
Manage rule definitions used by routes.
Methods: GET, POST
/api/v1/rules/{id}/
Retrieve or modify a specific rule.
Methods: GET, PUT, PATCH, DELETE
ACTIONS#
/api/v1/actions/
Manage Action configurations.
Methods: GET, POST
/api/v1/actions/{id}/
Retrieve or modify a specific Action.
Methods: GET, PUT, PATCH, DELETE
/api/v1/actions/{id}/parameters/
List parameters for an Action.
Methods: GET
/api/v1/actions/{id}/parameters/{parameterId}/
Update a specific Action parameter.
Methods: PATCH
/api/v1/actions/{id}/db/download/
Download the Action’s embedded DB file.
Methods: GET
/api/v1/actions/{id}/db/execute/
Execute SQL against the Action’s embedded DB.
Methods: POST
/api/v1/actions/{id}/wasm/download/
Download the compiled WASM bundle for the Action.
Methods: GET
/api/v1/actions/{id}/wasm/result/
Manage the latest WASM execution result.
Methods: GET, POST, PUT, DELETE
ROUTES#
/api/v1/routes/
Manage routing rulesets (routes).
Methods: GET, POST
/api/v1/routes/{id}/
Retrieve or modify a specific route.
Methods: GET, PUT, PATCH, DELETE
TASK-CONFIGS#
/api/v1/task-configs/
Manage background task configurations.
Methods: GET, POST
/api/v1/task-configs/{id}/
Retrieve or modify a specific task configuration.
Methods: GET, PUT, PATCH, DELETE
/api/v1/task-configs/{id}/action/execute/
Manually execute the action associated with a background task.
Methods: POST
/api/v1/task-configs/{id}/db/download/
Download the task’s SQLite3 database file.
Methods: GET
/api/v1/task-configs/{id}/db/execute/
Execute raw SQL queries on the task’s DB.
Methods: POST
/api/v1/task-configs/{id}/db/select/
Run read-only SQL queries and return rows from the task’s DB.
Methods: POST
/api/v1/task-configs/{id}/wasm/download/
Download the compiled WASM bundle attached to the task.
Methods: GET
Additional Notes#
Authentication is required for all API usage.
Access is restricted to mailboxes owned by the authenticated user.
When Would I Need to Use These APIs?#
Example: Build a Route via API (Rules → Actions → Parameters → Route)
Use the API to assemble a mail-processing pipeline end-to-end:
Create an Action Create the action that will run when a message matches your rules. Use
POST /api/v1/actions/and keep the returnedactionIdfor later.Configure Action Parameters - Inspect parameters:
GET /api/v1/actions/{actionId}/parameters/- Set values per parameter:PATCH /api/v1/actions/{actionId}/parameters/{parameterId}/(Repeat as needed for all required parameters.)Define Matching Rules Create one or more rules that describe when to trigger the action (e.g., subject contains “payment”, sender is “noreply@…”, has attachments). Use
POST /api/v1/rules/and collect the returned ``ruleId``(s).Create the Route Wire rules to the action so that matched emails invoke your action. Use
POST /api/v1/routes/providing the list ofruleId``(s) and the ``actionId.(Optional) Test the Flow - Send a test email into the system:
POST /api/v1/mailbox/{mailboxId}/testmail/- Verify processing records:GET /api/v1/mailbox/{mailboxId}/logs/
This flow is the most common: create action → set parameters → define rules → create route → test.
Example: Bob’s Background Task for Hourly Server Status Alerts
Bob wants to monitor server resource status every hour using a background task. He implements the following logic:
Query archive: Use
GET /api/v1/mailbox/{mailboxId}/archives/to fetch emails related to “server resource changes”.Track new emails: Use
POST /api/v1/task-configs/{taskId}/db/execute/to log each run into arecordstable in the SQLite3 database. Then compare current emails with past records to detect new incoming ones.Trigger alert if new email detected: If new emails exist, extract the latest message and use
POST /api/v1/task-configs/{taskId}/action/execute/to run the task’s action (e.g., sending to Telegram or WhatsApp).
This setup ensures Bob only receives one consolidated alert per hour, avoiding redundant messages and helping him focus on meaningful changes.
